BIQE OCR Server
User Manual
1. Introduction
About BIQE OCR Server
BIQE OCR Server complements modern high-speed document scanners with a highly optimised subsystem that applies optical character recognition (OCR) and Mixed Raster Content (MRC) compression to many different file types.
With BIQE OCR Server, you can easily create highly compressed and searchable PDFs without manual intervention. It has been built around a sophisticated Hot Folder system that processes files when they hit the source directory. As such, the BIQE OCR Server can easily be integrated into existing scanning workflows.
The exceptional speed offered by BIQE OCR Server is obtained by full parallelisation of processes, i.e. multiple pages are processed concurrently. Consequently, performance depends heavily on the machine that runs the software.
BIQE OCR Server is offered in the following configurations:
- 16 cores / 32 threads
- 28 cores / 56 threads
- unlimited cores/threads
1.1 Which license do I need?
Determining which license you need depends on two factors:
- The computer system you want to use to run BIQE OCR Server.
- The performance required
BIQE OCR Server is physically limited by the number of cores and threads (usually 2 threads for each core) available in the computer system. Hence, buying a more expensive license (allowing more threads to be used) only makes sense if the computer system contains these additional threads.
Usually, the number of threads doubles the number of available cores (please check your processor’s documentation). To inspect how many threads your current system has, open Device Manager in Windows and inspect Processors in the overview. It lists a processor for each available thread.
Another important consideration in determining which license (and perhaps which hardware) you need is the desired performance. By using a trial version of BIQE OCR Server, you can easily determine how much time your system requires to process a representative selection of typical documents in your workflow.
If it takes 10 seconds on average to process a page and your system can run 16 threads in parallel, it processes about 96 pages per minute (60 seconds / 10 seconds * 16 threads). If you use a document scanner that scans 200 pages per minute, you must upgrade your hardware and license to that level to keep up with your scanner’s speed. Otherwise, you will have to wait until your document scanner has finished.
To calculate, divide the number of pages per minute by the number of pages one thread can process. The result of that calculation yields the number of threads required to process the pages produced by the document scanner without delay.
E.g. 200 pages per minute / 10 pages per thread per minute = 20 threads.
Consequently, you will need a system with at least ten cores and two threads each. The only way to know how fast one thread can process one page is by trying it out with a trial version of BIQE OCR Server. However, modern systems (0-3 years old) usually process pages between 5-15 seconds per thread if both OCR and MRC compression are enabled.
1.2 Installation
Could you open the installation file and follow the procedure to install the BIQE OCR Server? You need administrator rights to complete the installation procedure successfully.
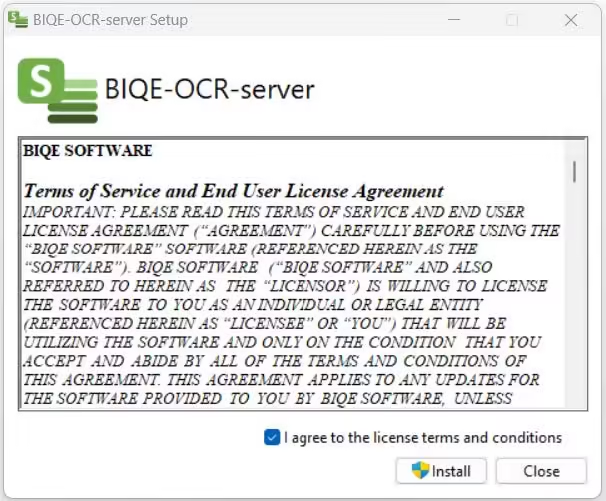
After reading and accepting the Terms of Service and the End User License Agreement, you press Install.
Windows will ask to install with administrator rights. After confirmation, the installation procedure starts, and the BIQE OCR Server, including some required packages, will be installed.
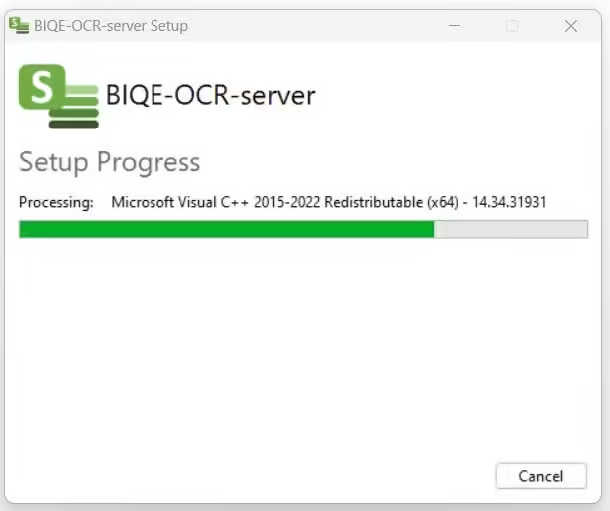
Upon finishing the installation successfully, you will be asked to restart your computer.
1.3 License Activation
When you start the BIQE OCR Server for the first time, it might indicate that it has not been activated yet.
The software cannot be used without activation. However, the activation procedure is smooth and convenient. To activate your product, click About in the menu.
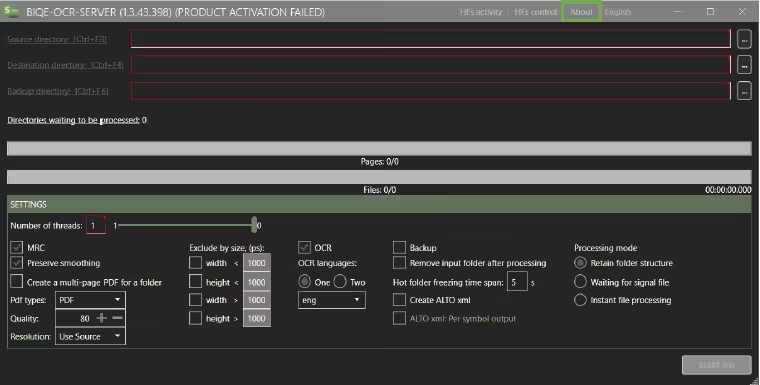
This opens a window that indicates that no license is activated.
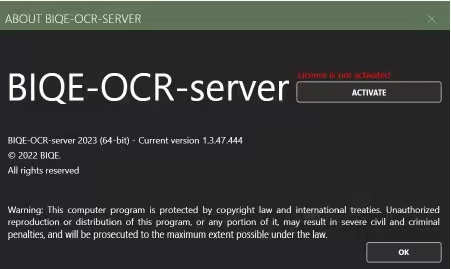
Enter your personal data and the license number you received to activate your license.
Click activate, and a message appears: Your license has been successfully activated.
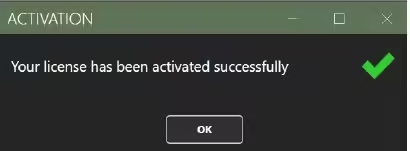
You will find your license details at the About page.
You are ready to use BIQE OCR Server.
1.4 Check activation status
To check the activation status, click About in the menu bar.
If activated correctly, the About window will show the license status, its type, and the maximum number of threads allowed under the current license.
Press OK to close the window.
2 Get started
This chapter provides a condensed overview of the BIQE OCR Server without going into detail. Subsequent chapters will give detailed descriptions.
Reading this chapter helps to understand the main components and the general workflow.
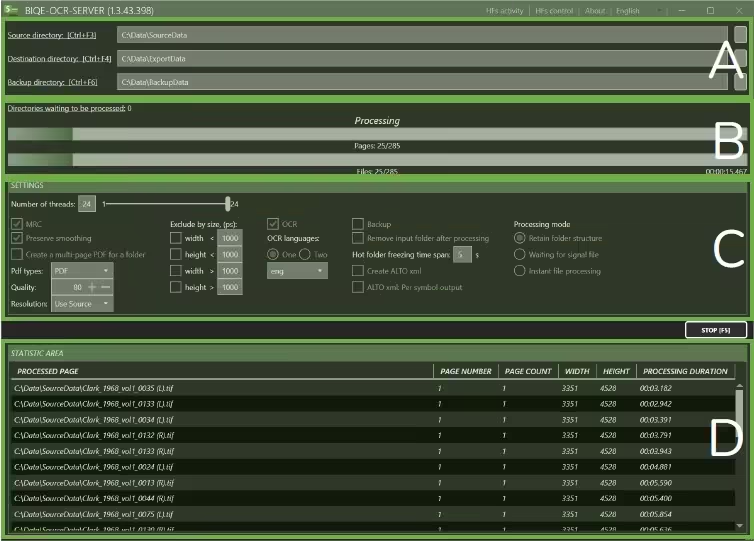
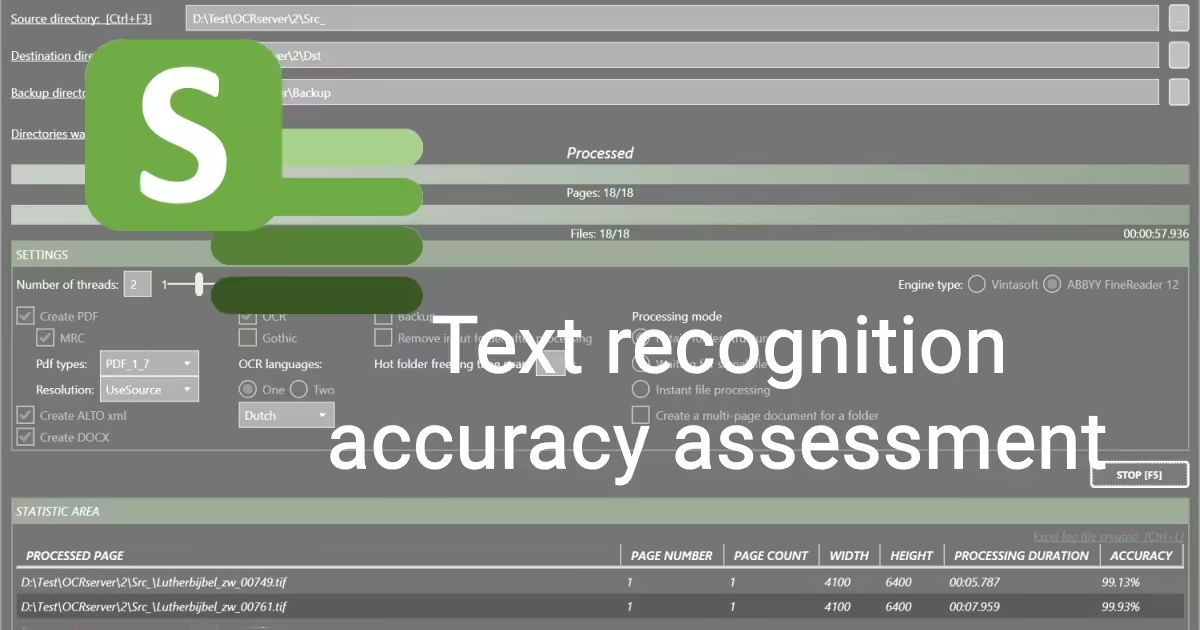
2.1 The user interface
- Directory management
- Progress
- Settings
- Statistic area
2.2 Directory management
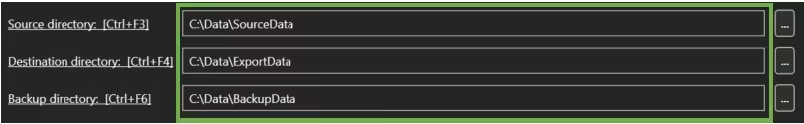
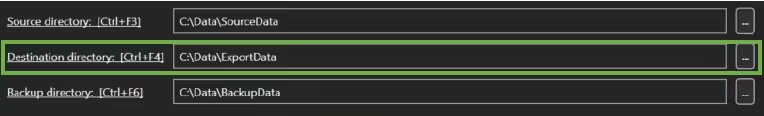
In the first section (A), three directories have to be defined:
- Source directory
- Destination directory
- Backup directory
The Source directory contains the files to be processed by the BIQE OCR Server and is the location of the Hot Folder. The Destination directory is where files will be written after processing. The Backup directory collects the original input files if the user activates the Backup option under Settings.
All three directories should be defined before starting the BIQE OCR Server.
2.3 Progress
The second section (B) provides instant access to what is going on while the BIQE OCR Server is running.
The first progress bar counts the number of pages processed, while the second bar counts the number of files processed. If every file contains only one page, both bars should progress equally.
However, they will differ in the case of multipage input files.
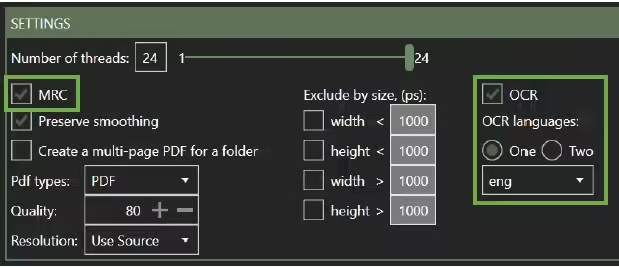
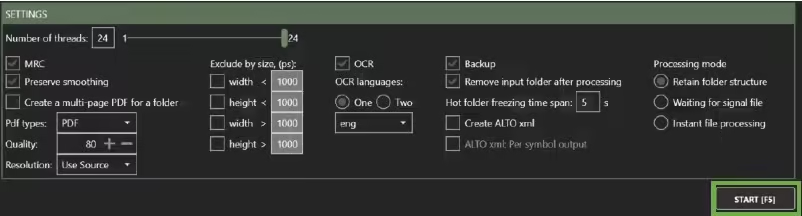
2.4 Settings
The settings section (C) is the critical panel with all the definitions of what the BIQE OCR Server will do. Here, you define the actions to be performed and the rules to be applied. Please start with the default settings to get started.
The two main functions of the BIQE OCR Server are defined here:
- Applying MRC Compression
- Applying one or two OCR languages
All details about the settings are elaborated on in Chapter 4.
2.5 Statistic area
The Statistic Area section provides insights into the pages processed. Ordering on one of the different columns allows you to identify outliers easily, such as pages with a different width or height or page processing time.
2.6 First-time set up
To start your first run, you must fill in the directories first (cf. 2.3). Enter the directory paths by typing them or pasting them into the path sections.
You can also click on the three bullets and select the folder you want to use.

After assigning the directories, proceed to select your preferences in the Settings window below and click the START button to begin the process.
3 Directory Management
In this chapter, we explain how directories operate in BIQE OCR Server (A). BIQE provides advanced interactions with existing systems and pipelines. However, it is important to understand how the directories selected interact with given settings.
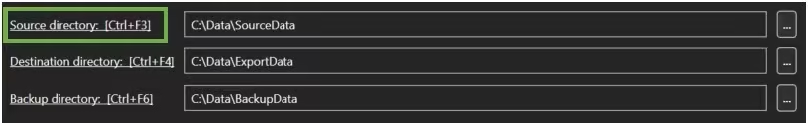
3.1 Source directory
The Source directory is a single directory in your computer system. This directory functions as a Hot Folder.
Tip: Create the source folder on the fastest available disk, as the fastest reads will increase the BIQE OCR Server’s performance.
The Source directory can be defined in two ways:
- By typing or pasting the path
- By clicking the three bullets next to the input field
To view the contents of the Source directory, click on the URL or use the shortcut CTRL + F3. This opens the directory in Windows Explorer.
Two settings have an effect on the way the BIQE OCR Server deals with the Source directory:
- Remove the input folder after processing
- Processing mode
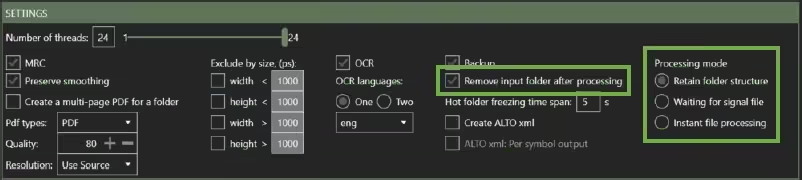
3.1.1 Remove the input folder after processing
Delete input folder after processing determines whether files in the Source directory are deleted after processing. If BIQE OCR Server is part of an automatic pipeline, it is advisable to delete the files after processing to prevent the Source directory to become cluttered.
Enabling the Delete input folder after processing will permanently remove your input files. Check the Backup option to ensure that your original files are saved!
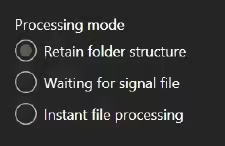
3.1.2 Processing mode
BIQE OCR Server has three different Hot Folder functionalities for processing files in the Source Folder. You can select one Hot Folder functionality per process.
- Retain folder structure
- Waiting for signal file
- Instant file processing
The retain folder structure creates an exact copy of the Source directory in terms of the structure of (sub)folders and files. It allows you to organise your data before processing them.
Wait for signal file keeps the Hot Folder inactive even after you click the START button until an empty complete.txt file is created or copied into the Source directory.
Instant file processing turns your Source directory into a Hot Folder that processes files as soon as they enter this directory. This can be very useful in automatic pipelines.
Each of the Processing settings is further elaborated in Chapter 5.
3.2 Destination directory
The Destination directory is where all BIQE OCR Server output is written. Using a fast hard drive for this directory will improve the overall performance of the BIQE OCR Server.
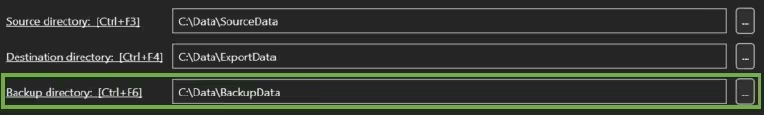
3.3 Backup directory
The Backup directory is the folder where all the original input files are written. It is generally advisable to use the Backup option to keep the original files after processing.
4 Progress
This section explains the progress indicators available in BIQE OCR Server (B). In addition to the general progress bars in the main window, the BIQE OCR Server provides two other windows to monitor the process: HF’s activity and HF’s control. This chapter explains both of these additional windows.
4.1 Main window progress bars
The main window shows two different progress bars. As soon as a process is started, the system counts the number of files and the pages available. The first progress bar keeps track of the number of pages to be processed. This bar provides the most accurate indication of the process’s progress.
The second progress bar counts the number of files to be processed. If each file contains only one page, the two bars synchronise.
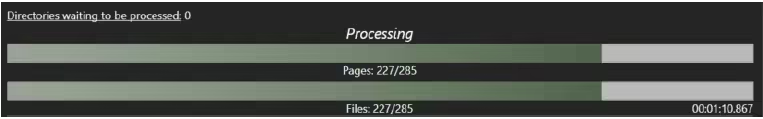
Two other indicators are available next to these two: a directory count of waiting directories in the upper left corner of the Progress section and an indicator of elapsed time in the lower right corner.
Clicking the waiting directories URL opens a new window with the directories listed. They will be processed after the current process ends.
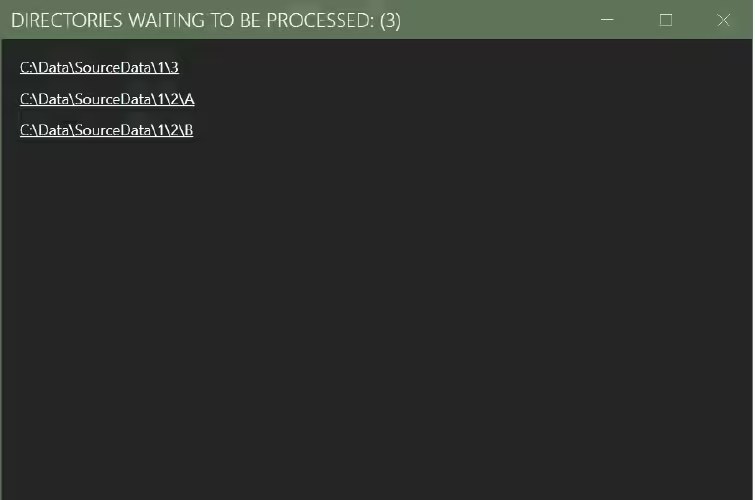
Waiting directories happen when files are added to a directory after it has been frozen (cf. 4.2).
4.2 HFs activity

HFs activity provides insight into the Hot Folder’s (HFs) activity. This is relevant in an active document instream from, e.g. a document scanner.
When large multi-page PDFs are produced, it takes time to write the complete file. To avoid the situation where the BIQE OCR Server tries to process a file or a folder while they are still incomplete, this Hot Folder system works with a dual structure: folders that change (i.e. files are still being written) and folders that are frozen because the creation of (sub-)folders and files has been completed.
The parameter to control the period in which no more (sub)folders and files are added and the process can be completed can be set with the Time span freeze folder. The integer entered refers to the number of seconds that must elapse without changing the folder before the folder is processed (frozen).
Any change after the set time span is treated as a new process.
With HF activity, you get real-time insight into which directories are frozen and which ones are not.
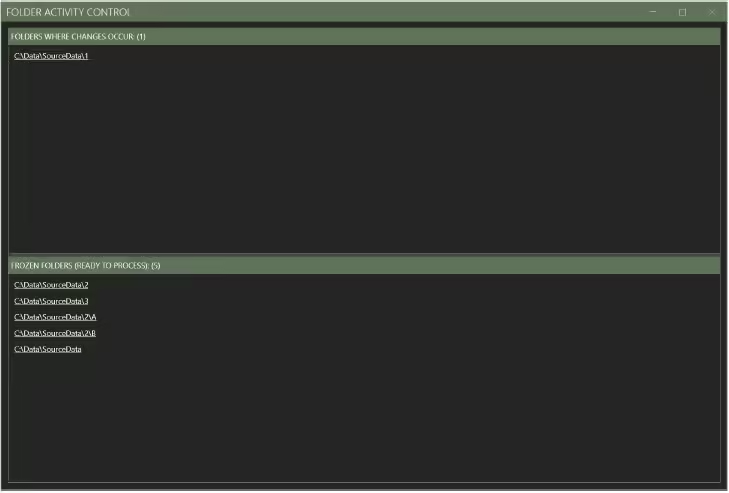
4.3 HFs control
The HF control screen gives you insight into the directories currently being processed and those that are finished. This screen is handy if the BIQE OCR Server runs in an automatic pipeline. It provides insight into all processes that have been started since the START button has been pressed.
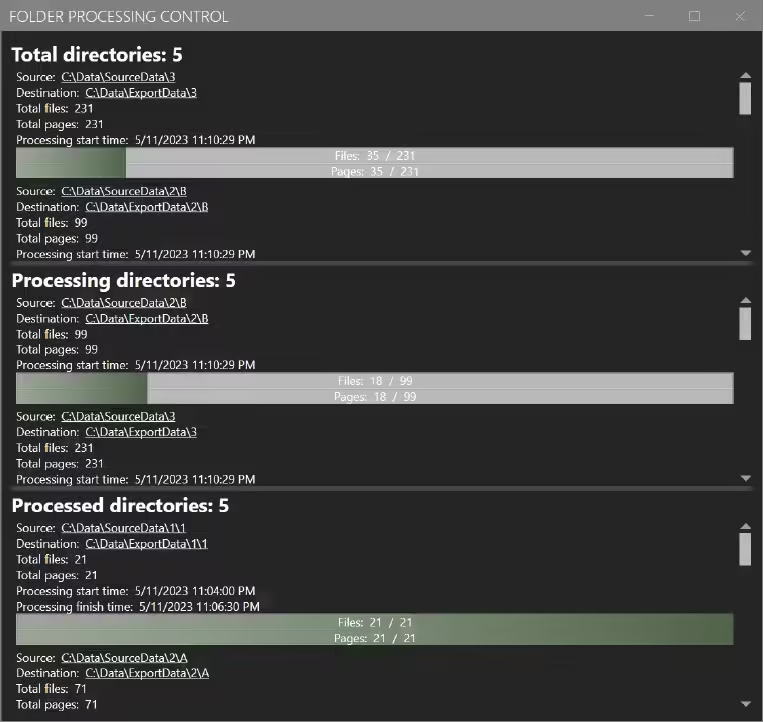

5 Settings
In the settings section (C), you define the specific requirements for the task you want to perform.
This section explains each requirement one by one.
5.1 Number of threads
BIQE OCR Server was created with a focus on maximum performance. In processing files, all available threads of your system can be used. The number of threads available depends on the number of physical cores (usually 2 threads each) available in the computer system and the license.

The license determines the maximum number of threads available, but your computer system determines the actual number. If you bought a license for 24 threads, but your system has 8 cores with 16 threads, then the maximum number of threads to be used is 16 threads.
If no other (demanding) processes besides BIQE OCR Server are running, you can safely use the maximum number of threads available. If the BIQE OCR Server is used in an active production pipeline where the same computer system is actively receiving files from, e.g., a document scanner, it is recommended to stay at least 2 threads below the maximum to leave capacity to the other process.
5.2 MRC compression
One of the key functionalities of the BIQE OCR Server is its capability to apply Mixed-Raster Content (MRC) Compression to input files. BIQE OCR Server offers this functionality without limitation.
Until PDF 1.4, JPEG compression was used, while JP2 compression was applied in later versions. Although the common JPEG/Jp2 compression works well with colour images, it performs poorly on text, resulting in unpleasant artefacts. Ideally, the text should have sharp edges to be optimally readable.
MRC Compression has two major advantages over JPEG/Jp2 compression:
- it significantly reduces the size of the PDF file
- it keeps the text readable and clean
As a result, you need less storage capacity, and transferring files requires much less time because the files you send are smaller.
How does MRC work? MRC Compression is divided into three layers: A binary layer (text), which is stored in high resolution using the JBIG2 algorithm; A highly compressed background layer, which contains the background image after splitting the contents of the previous layer; and a foreground layer, which contains the colours of the binary layer. The final file size reduction rate depends on your chosen Quality and Resolution.
5.3 Preserve smoothing
Preserve Smoothing is a compression algorithm that smooths the edges of letters, making the letter more readable on the screen. This setting is highly recommended for text documents.
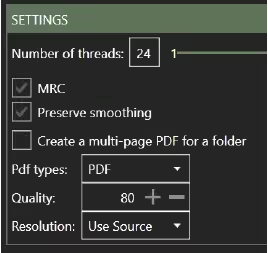
5.4 Create a multi-page PDF for a folder
Enabling this setting instructs BIQE OCR Server to treat a directory with files as one document. As a result, one single multi-page PDF will be created from all files available within the directory.
5.5 PDF types
BIQE OCR Server features all common PDF types. By default, the BIQE Server chooses PDF version 1.7, but you can also select another PDF type and version to meet your requirements.
5.6 Quality
The Quality option sets the compression percentage relative to the original. 1 indicates the highest compression rate with the lowest image quality; 100 is uncompressed and preserves the highest image quality. For text documents, we recommend a compression factor of 15 to have a good balance between compression and image quality. Documents with images, will require a higher quality to keep a convincing result.
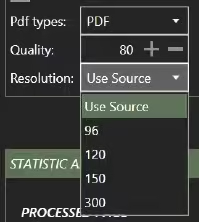
5.7 Resolution
The used source keeps the original dpi except for documents with a resolution higher than 600 dpi, which are down-sampled to 300 dpi.
This value can be upscaled or downscaled according to your needs. Currently, the following common values can be used:
- 96 dpi
- 120 dpi
- 150 dpi
- 300 dpi
5.8 Exclude by size
BIQE OCR Server allows you to exclude images with specific dimensions from OCR. You can both exclude images that are below a certain threshold (<) or pictures that are above a certain threshold (>). Each rule can be set individually by checking the checkboxes.

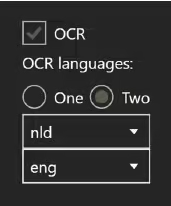
5.9 OCR
BIQE OCR Server allows you to use up to two OCR languages simultaneously.
You must select the OCR checkbox for a searchable PDF and choose one or two OCR languages.
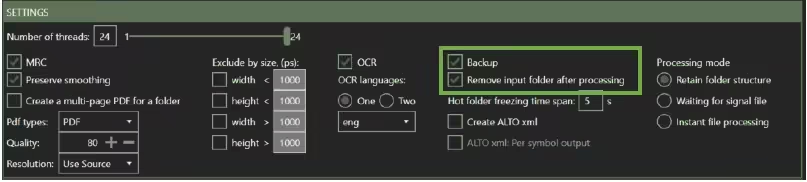
5.10 Backup
If you check the Backup option, the original files from the Source directory are copied to the set Backup directory.
Tip: We recommend always checking the Backup option in combination with the Delete input directory after processing.
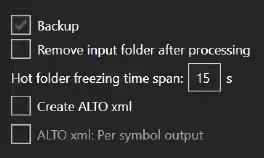
5.11 Remove input folder after processing
This option causes the Hot Folder (Source directory) to be emptied after processing the files.
If you do not have the Backup option checked, the original files will be permanently deleted!
5.12 Hot folder freezing time span
The Hot folder freezing time waits to process files until the set number of seconds (a maximum of 90) has passed. This prevents files from being processed while still being written to the source directory.
The default is 5 seconds. However, if very large files (> 100 MB) are written to the source directory, increasing the number of seconds to a safe zone is important.
5.13 Create ALTO xml
ALTO stands for Analyzed Layout and Text Object. The document consists of both the recognised text and the precise text positions of the text on the image.

This allows you to inspect the text layer easily without the need to extract it from the PDF.
Be aware, however, that enabling this function will create an XML file in addition to the PDF file, resulting in 2 output files for one input file.
5.14 ALTO xml: Per symbol output
BIQE OCR Server offers the option to save the ALTO xml at the TOKEN level in addition to the ALTO xml option at the WORD level. Enable this checkbox if you have that specific requirement.
5.15 Processing mode
BIQE OCR Server offers three processing modes that define the behaviour of the Hot Folder more precisely.
5.15.1 Retain folder structure
This option preserves the original folder (and subfolder) structure according to the Source folder. After processing, the folder structure of the Destination folder will be identical to that of the Source folder.
If any files are added to the Hot Folder during processing, it is important to set the Hot Folder freeze time properly, especially if the files are large. If the freezing time expires without adding more files to the Hot Folder, the folder will be locked and all changes will be considered a new process.
5.15.2 Waiting for signal file
In this Hot folder mode, file processing will not begin until an empty complete.txt file is created/copied into the Source directory. This mode does not allow nested folder structures!
This mode is handy when input data needs to be processed in batches and when the scanner produces a signal file after scanning a batch of documents.
TIP: A bank can efficiently process customer data separately by copying the complete.txt to the Source Directory after processing each customer.
5.15.3 Instant file processing
In this Hot folder mode, file This mode processes every single file as soon as it hits the Hot Folder, as long as the START button is active. This option does not allow for multi-page PDF creation, nor does it permit automatically removing files from the Source directory. After processing each customer.
6 Statistic Area
Finally, the BIQE OCR Server provides a real-time interface to understand processed page data (D). In addition to the file name, the page number, total number of pages in the file, width and height, and processing time are listed.
You can click on each column to reorder its content. That way, you can easily detect deviations in time and size. Pages that are processed quickly usually have little or no text that needs recognition. Organising the processed files by processing time allows you to find the empty pages easily.
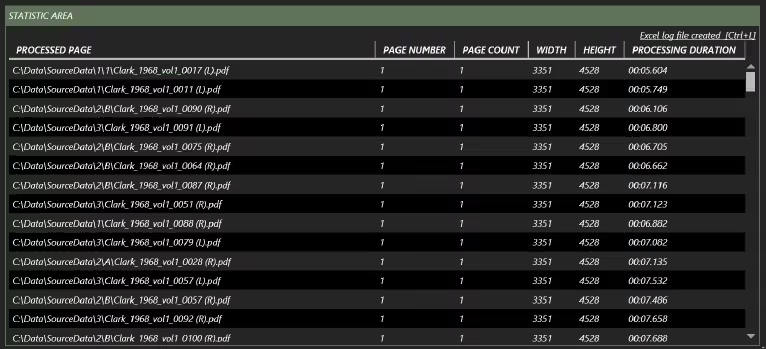
The full logs are written in an Excel file that can be accessed in the upper right corner or by pressing the shortcut CTRL + L. Log files are written in a separate ’log’ directory in the Destination directory.
If you have any questions please mail us:
info@biqe.biz
Postal address
Meerweg 17
8313 AK Rutten
Netherlands
BIQE OCR Server
- Unlimited Speed
- Unlimited MRC PDF compression
- Fully scalable according to available cores/threads
- Unique hotfolder processing